Introduction:
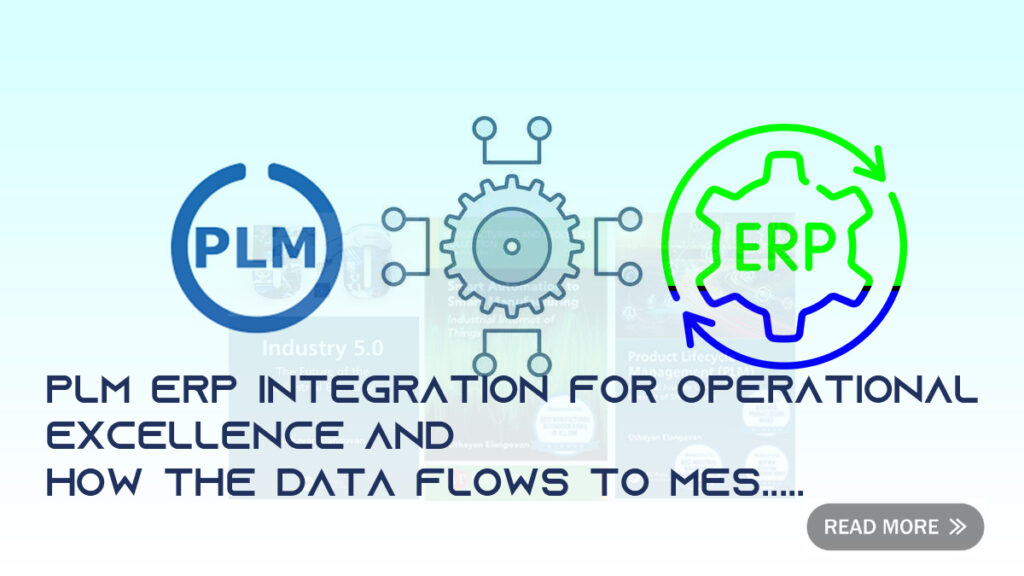
In today’s competitive business landscape, organizations across various industries strive for operational excellence to enhance productivity, streamline processes, and maximize profitability. To achieve these goals, the integration of Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems has emerged as a critical initiative. This integration facilitates seamless data exchange and synchronization between the two applications, enabling organizations to optimize their business processes and improve decision-making. In this article, we will explore the challenges, risks, mitigation strategies, business benefits, and value associated with integrating PLM with ERP.
1. Integration Challenges:
a. Technical Incompatibility: PLM and ERP systems often employ different data models, formats, and architectures, leading to integration complexities.
b. Data Synchronization: Maintaining consistency and accuracy between PLM and ERP databases, especially during product design changes and updates, can be challenging.
c. Process Alignment: Aligning the distinct workflows and business processes of PLM and ERP systems requires careful planning and coordination.
2. Integration Risks and Mitigation:
a. Data Integrity and Security: The integration process must address data integrity, confidentiality, and access control to safeguard sensitive product and business information.
Example: A manufacturing company integrates its PLM and ERP systems, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access critical design and production data. Encryption and access control measures are implemented to protect intellectual property from unauthorized access.
b. System Downtime and Performance: Integration can introduce risks of system downtime and performance degradation, disrupting business operations.
Example: An automotive manufacturer plans the integration during a scheduled maintenance window to minimize the impact on production activities. Extensive testing and simulation are conducted beforehand to identify and resolve any performance bottlenecks.
c. Change Management: The integration may require process reengineering, organizational restructuring, and user training, which can face resistance and slow adoption.
Example: A medical device company communicates the integration benefits to employees and provides comprehensive training programs to familiarize them with the new integrated workflows. This mitigates resistance and accelerates the adoption of the integrated system.
3. Business Benefits:
a. Enhanced Collaboration and Visibility: Integration enables seamless collaboration between cross-functional teams, such as engineering, manufacturing, and supply chain, fostering better communication, reducing errors, and improving decision-making.
Example: By integrating PLM with ERP, a consumer electronics company enables real-time visibility into product design changes, allowing the manufacturing team to plan production activities accordingly, reducing rework, and improving time-to-market.
b. Streamlined Processes and Reduced Costs: Integration eliminates redundant data entry, streamlines processes, and reduces manual errors, leading to improved operational efficiency and cost savings.
Example: A fashion apparel company integrates PLM and ERP systems, automating the transfer of design specifications, materials, and bills of materials, thereby reducing time-consuming manual data entry and minimizing errors in the production process.
c. Improved Product Quality and Compliance: Integration facilitates the seamless flow of product and quality data between PLM and ERP systems, enabling organizations to ensure regulatory compliance, track product genealogy, and maintain quality standards.
Example: A pharmaceutical manufacturer integrates PLM with ERP, allowing seamless traceability of raw materials, equipment calibration records, and batch genealogy, thereby ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements and improving product quality.
4. Business Value and Need for Integration:
a. Holistic View of Product Lifecycle: Integrating PLM with ERP provides a unified view of the product lifecycle, enabling organizations to make data-driven decisions and optimize processes throughout the product development and manufacturing stages.
b. Efficient Resource Planning: Integration enables organizations to align resources, such as materials, equipment, and labor, with the product design and production requirements, ensuring efficient resource utilization and reducing costs.
c. Faster Time-to-Market: By eliminating data silos and enabling real-time collaboration, integration accelerates product development cycles, reducing time-to-market and enhancing competitive advantage.
Data Sharing and Flow to MES:
In the integrated PLM-ERP environment, data is shared between the two applications at various stages of the product lifecycle. For example:
1. During the design phase, PLM provides product specifications, bills of materials, and engineering change information to ERP for resource planning and production scheduling.
2. In the manufacturing phase, ERP sends work instructions, production status, and quality data to PLM for real-time monitoring, analysis, and feedback.
3. As the product moves towards the shop floor, data flows from ERP to Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), providing instructions for operators, capturing production data, and enabling real-time visibility into shop floor activities.
Conclusion:
The integration of PLM with ERP offers numerous advantages and is crucial for organizations aiming to achieve operational excellence. Despite the challenges and risks involved, careful planning, robust change management, and adherence to best practices mitigate potential pitfalls. The seamless flow of data between PLM, ERP, and MES systems optimizes collaboration, streamlines processes, improves decision-making, and drives business growth. By embracing this integration, organizations can unlock the synergies between these applications and gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic business environment.
Contact us today to drive your business forward! As a trusted partner, we offer expert implementation, upgrade, rollout, and support services for OpenBOM PLM and PTC Windchill PLM. Whether you’re an SME or a discrete manufacturer, unlock the full potential of your business with our tailored solutions. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to optimize your operations and stay ahead of the competition. Get in touch with our team now!