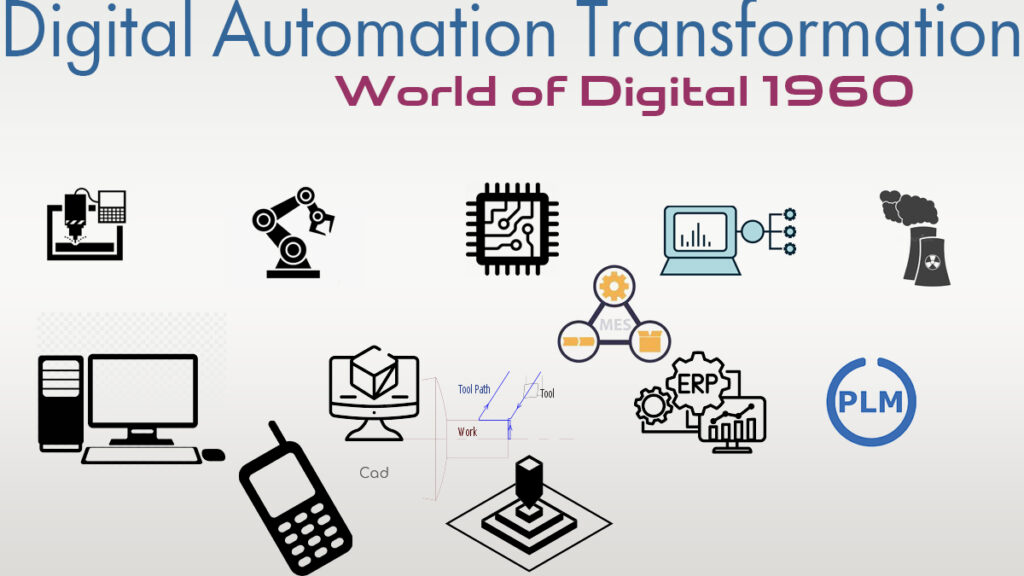
Digital Automation Transformation is defined by the spread of automation and digitization with using electronic devices along with computers, the creation of the Web, besides the exploration of nuclear energy.
- Introduction:
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
- Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM)
- Rapid Prototyping
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
- Industrial Robots and Programmable Logic Controllers(PLC)
- Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA)
- Conclusion: Industry 3.0 to Industry 4.0
Introduction:
Manufacturing enterprises across the globe have witnessed a remarkable transformation with the advent of Industry 3.0 – the era of digital automation. Industry 3.0 started gaining toughness and beginning to form the 21st century. Internet as well as billions of affiliated as well as functional devices are rapidly reconsidering communication. Using hardware (Semiconductors) and Information Technology (Mainframe Computing, Personal Devices, and also Web) promote activity in independent generation.
This era observed the rise of electronics like never in the past, from computer systems to new innovations that allow the automation of commercial processes. Improvements in telecoms blazed a trail for prevalent globalization, which consequently allowed industrial sectors to offshore production to low-cost and radicalize business models worldwide.
This revolution brought about by the integration of computer-aided technologies has significantly impacted manufacturing processes, leading to improved efficiency, reduced production time, and enhanced product quality. Key technologies that played a crucial role in this transformation include CAD, CAM, Rapid Prototyping, ERP, MES, PLM, Industrial Robots, PLC, and SCADA. Let’s explore how these innovations have shaped Industry 3.0 and paved the way for Industry 4.0.
Given that the beginning of Production, Factory proprietors are tried to find rise of Performance and also lower cost. This resulted in automating the production line, which becomes the lower line of Automation.
Automation causes much better effectiveness. Human beings makes mistake and constantly not normal, automation almost gets rid of blunder, rise efficiency and also permits much better security in addition to controlled manufacturing procedure. Details is generated throughout the process as well as also used by countless elements along the line handling the operations. Mechanical automation showing up in the commercial center in the 1970’s.
CNC Device did a vital job in the establishing divisions for mechanizing the treatment making use of Computer systems to take care of machine tools. Later fast prototyping gets its relevance in the brand-new product growth made use of amidst the academic phase. Fast prototyping is a party of therapies utilized to quickly make a scale variation of a physical part or get together making use of three-dimensional computer sustained synopsis details.
Rise of CAD, CAM, Rapid prototyping, ERP, MES, PLM, Industrial Robots, PLC later followed by SCADA made a huge impact on the manufacturing enterprises across the globe and named as digital game changer of the manufacturers.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
One of the first significant advancements in Industry 3.0 was the introduction of CAD and CAM systems. CAD revolutionized the way product design was done, allowing engineers to create detailed 2D and 3D models on computers. This digital approach drastically reduced the time required to design complex products, enabled rapid iterations, and facilitated collaboration among design teams.
Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM)
CAM, on the other hand, brought automation to the manufacturing process. By utilizing the digital designs created in CAD, CAM software controlled machines like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) mills and lathes, making it possible to produce precise and intricate components with minimal human intervention. This integration of design and manufacturing led to increased productivity and accuracy, transforming the industry.
Rapid Prototyping
Rapid Prototyping, also known as 3D printing, was a game-changer in Industry 3.0. It allowed manufacturers to create physical prototypes of products directly from digital designs. This technology accelerated the product development process, as designers and engineers could now quickly validate and test their ideas before moving to full-scale production. By reducing prototyping time and costs, rapid prototyping fostered innovation and gave rise to a more agile manufacturing environment.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
With the growth of digital automation, manufacturing enterprises faced the challenge of managing complex processes efficiently. ERP systems came to the rescue by integrating various aspects of a business, such as inventory management, production scheduling, financials, and human resources, into a single, centralized software platform. This integration streamlined operations, improved data visibility, and enabled better decision-making.
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
MES, on the other hand, focused on optimizing manufacturing processes. It provided real-time monitoring and control over shop floor activities, ensuring that production schedules were adhered to, and resources were utilized optimally. By linking production data with ERP systems, MES facilitated seamless communication and collaboration between different departments, leading to higher productivity and reduced lead times.
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM)
PLM systems played a critical role in managing the entire lifecycle of a product, from ideation and design to manufacturing, service, and disposal. These platforms allowed manufacturers to track product data, manage revisions, and maintain version control, ensuring that the right information reached the right stakeholders at the right time. PLM facilitated collaboration across geographically dispersed teams and suppliers, driving innovation and accelerating time-to-market.
Industrial Robots and Programmable Logic Controllers(PLC)
Industrial robots brought about a manufacturing revolution through the automation of monotonous and hazardous tasks These robots, equipped with advanced sensors and programming capabilities, improved production speed and precision while reducing human errors. PLCs, on the other hand, acted as the brain of manufacturing systems, controlling and coordinating various machines and processes.
Together, industrial robots and PLCs transformed the production landscape, enabling manufacturers to achieve higher volumes, consistent quality, and cost-effective operations. Moreover, robots provided the flexibility to adapt to changing product demands, making manufacturing processes more agile and responsive.
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA)
SCADA systems played a crucial role in Industry 3.0 by providing real-time monitoring and control over industrial processes. These systems collected data from sensors and equipment on the shop floor and presented it to operators and managers in a visual format. This allowed for timely decision-making, quick issue identification, and enhanced process optimization.
SCADA also facilitated remote monitoring and control, enabling manufacturers to manage multiple facilities from a central location. The combination of SCADA with other digital automation technologies created a smart manufacturing environment, where data-driven insights drove continuous improvement and operational excellence.
Conclusion: Industry 3.0 to Industry 4.0
Digital Automation transformation modern technologies paved the path to Industry 4.0, which enable to automate a whole manufacturing procedure – without human aid. Known examples of this product design process automation using CAD integration with PLM and manufacturing process automation utilizing PLM integration with ERP. Process control system automation using PLC, SCADA along with robotics that execute configured series with minimal human involvement.
This transformation laid the foundation for Industry 4.0, which is characterized by cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, artificial intelligence, and advanced robotics. Industry 4.0 further pushes the boundaries of digital automation, aiming to create fully connected and intelligent manufacturing ecosystems, where machines communicate, analyze, and optimize processes in real-time.
As the manufacturing industry progresses into the era of Industry 4.0, the digital game-changers of Industry 3.0 will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of manufacturing, driving innovation, and ushering in new possibilities for the global economy.