
Introduction:
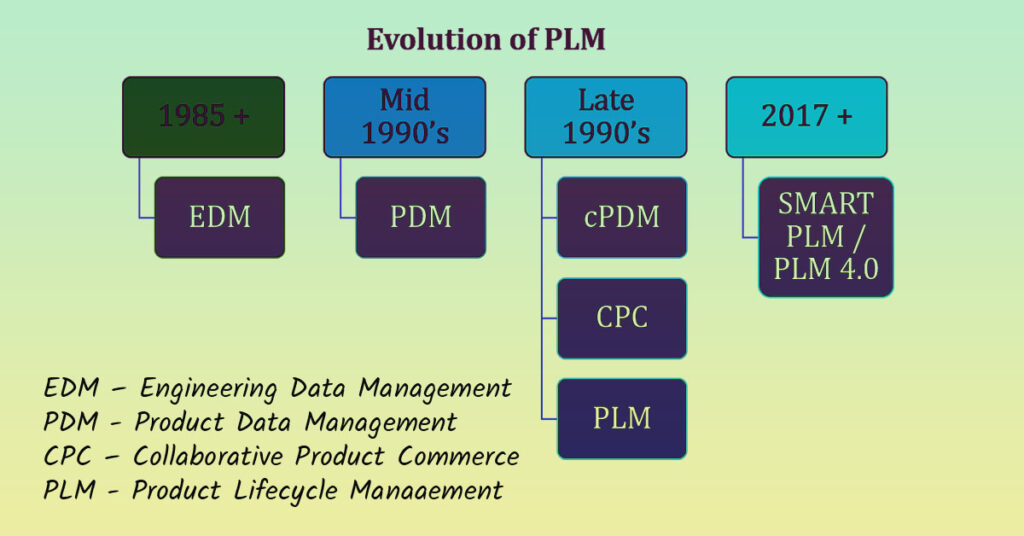
Product Data Management (PDM) or Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is the normal scenario for any manufacturing enterprises while starting their digital transformation. Choosing the exact solution based on the requirement is a challenging job. So as a thumb rule before going for a concrete decision, understand the difference between PDM and PLM as well how both of complement each other.
A system used during product design to store and retrieve data to ensure information consistency throughout the life cycle of a product. It benefits use of concurrent engineering while maintaining control of data and distributing it automatically to the people who need it – when they need it.
PDM works on the concept of Check In and Check Out Mechanism.
Workspace: private area where the user can work on the objects, create new ones. This area is not accessible by other users. Each time a user wants to work on a product data, this object has to be brought into his workspace.
Commonspace: Shared area accessible to all authorized users. This is where checked in objects go.
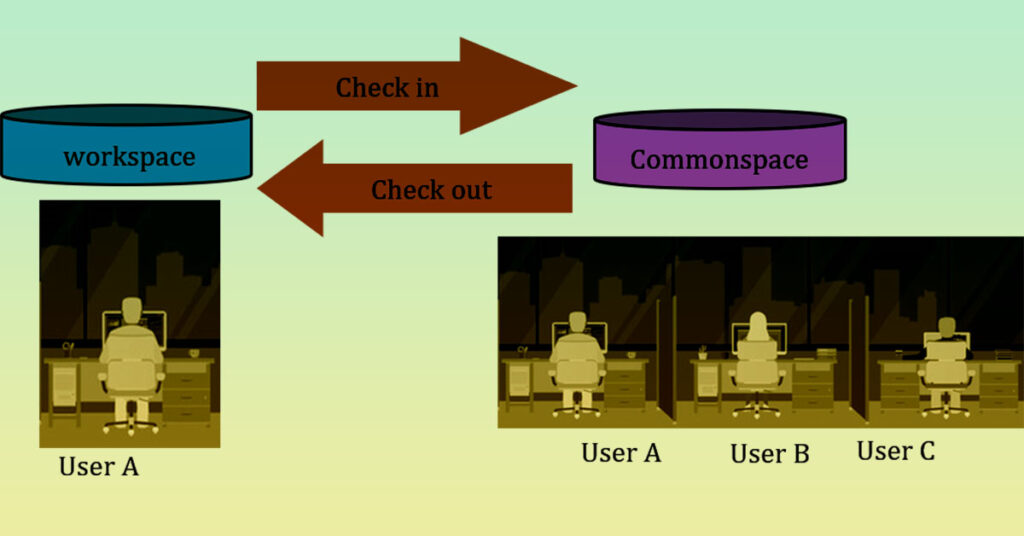
So PDM is a centralized information monitoring system made use of to manage new product related CAD data, its features, iteration and also its connected business processes. PDM handles, utilizes, as well take advantage of design and also development process data. Manufacturers of all sizes (small to medium to large to OEM) all gain from PDM. Product manager recognizes the details of the design information, and have the ability to utilize them in item development. It proactively constructing means to accumulate and also take care of information, and utilizing it to develop a final product, supplied to the end customer. Every change is tracked, because of the fact that the variant control is structured, it’s straightforward to go back to a previous variation.
PDM is the core of PLM.
PLM is a business strategy that helps companies share product data, apply common processes, and leverage corporate knowledge for the development of products from conception to retirement across the extended enterprise. PLM develop an incorporated digital platform to trace the NPD/NPI process. PLM is most likely to aid product design obtain their CAD files regulated, process engineering change orders quicker, increase component reuse, and so on but what will the overall company effect be? By carrying out a PLM system, business can simplify and also reduce each stage of the product development process is consider a crucial success variable.
Products are becoming more advanced and smarter. Enterprise’s need a better model to support their product development in this competitive era. PLM manage all aspects of the product lifecycle, from concept design to product retirement.
- Efficiency improvements
- Improving development for new products
- Reduced costs
- Increase productivity
- Improved quality of products
PLM is required to incorporate all task towards the design, manufacturing as well assistance of the product. PLM enable superior product administration from concept to retirement. PLM can assist individuals improve their understanding of how products are developed, built as well as serviced.
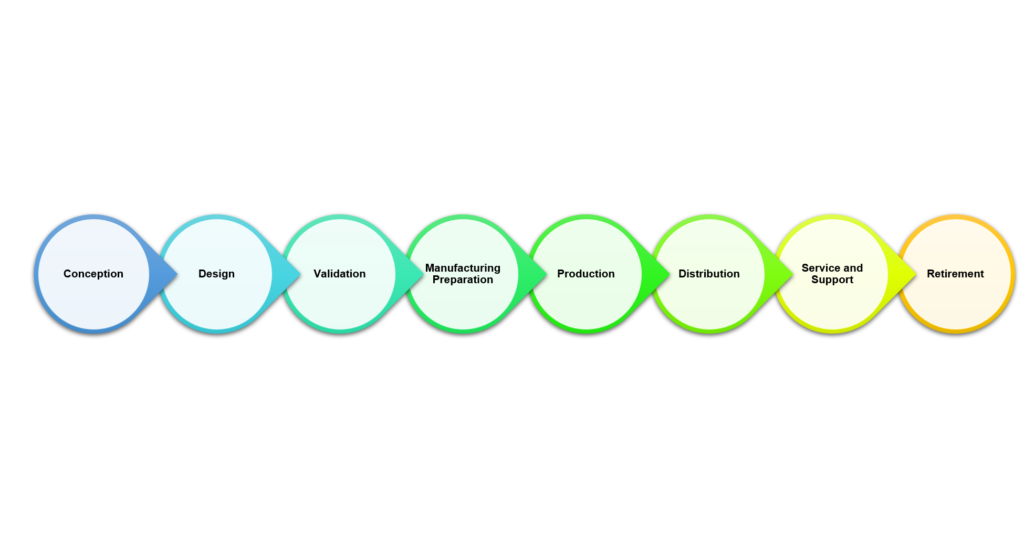
PLM Process Flow
Conception
What Happens: Ideas are born, and initial concepts are sketched out.
Benefits: Sparks innovation and captures creative ideas.
Design
What Happens: Detailed designs and CAD models are developed.
Benefits: Enhances accuracy and fosters team collaboration.
Validation
What Happens: Prototypes are tested to ensure they meet standards.
Benefits: Identifies potential issues early, saving time and costs.
Manufacturing Preparation
What Happens: Manufacturing processes and tools are set up.
Benefits: Streamlines production planning and ensures readiness.
Production
What Happens: The product is manufactured.
Benefits: Ensures quality and efficiency in production.
Distribution
What Happens: The product is distributed to customers.
Benefits: Optimizes supply chain and enhances customer satisfaction.
Service and Support
What Happens: Post-sale support and maintenance.
Benefits: Increases customer satisfaction and gathers feedback.
Retirement
What Happens: The product is phased out, recycled, or disposed of.
Benefits: Complies with regulations and captures insights for future products.
When it comes to selecting a PDM/PLM system, there are many factors to consider. It is important to choose the right system that meets your business objectives and enables you to effectively manage your product lifecycle. The right PLM system can help you manage product development and production, streamline processes, reduce costs, and increase efficiency. It’s important to take the time to evaluate different PLM systems and determine which one is best suited for your needs.
PDM vs. PLM: Key Features and Benefits
Product Data Management
Core Focus:
- Manages product data and documentation.
- Primarily used by engineering teams.
Key Features:
- Centralized Data Repository: Secure storage for CAD files, drawings, and specifications.
- Version Control: Ensures accurate tracking of revisions and updates.
- Access Control: Regulates who can view or edit data.
- Search and Retrieval: Quick access to needed documents and data.
- Workflow Automation: Streamlines approval processes for engineering changes.
Benefits:
- Improved Collaboration: Engineers can easily share and access up-to-date information.
- Error Reduction: Minimizes mistakes with controlled data access and version tracking.
- Efficiency: Speeds up design processes with automated workflows.
- Data Security: Protects intellectual property with robust access controls.
Product Lifecycle Management
Core Focus:
- Oversees the complete journey of a product, from initial idea to final disposal.
- Integrates data and processes across the organization.
Key Features:
- End-to-End Product Management: Oversees every phase of the product lifecycle.
- Cross-Department Integration: Connects R&D, engineering, manufacturing, quality, and service teams.
- Advanced Analytics: Provides insights for decision-making and continuous improvement.
- Change Management: Facilitates comprehensive change control across the product lifecycle.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures adherence to industry standards and regulations.
Benefits:
- Holistic View: Offers a complete perspective on product development and lifecycle.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Promotes teamwork and information sharing across departments.
- Innovation Acceleration: Drives faster and more efficient product development.
- Cost Reduction: Decreases costs by optimizing resources and processes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Helps meet legal and regulatory requirements efficiently.
Why Choose PDM or PLM?
Choose PDM if you need:
- A robust system for managing engineering data and documents.
- Enhanced control over CAD files and design processes.
Choose PLM if you need:
- Comprehensive management of the entire product lifecycle.
- Integration across various business functions and advanced analytics for decision-making.
Final Thoughts
Both PDM and PLM are powerful tools that cater to different needs within an organization. PDM excels in managing engineering data, ensuring version control, and streamlining design workflows. In contrast, PLM offers a broader scope, overseeing the entire product lifecycle, promoting cross-departmental collaboration, and driving innovation. Understanding the unique features and benefits of each can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your business goals.
Recognizing the difference in addition to greater possibility for PLM that how it is most likely to add worth to enterprise. When thinking about the requirements for PLM, you ought to think about the amount of gross profits as well as the variety of staff members, CAD users, as well as non-CAD users that require accessibility to product design data. An efficient PLM program, with well-defined connected campaigns and a purposeful carrying out plan, sets the ground for an effective transformation. In current scenario, SME manufacturers can opt for cloud-based PLM to compete in this smart connected world.

