Understanding the Role of MPM in Modern Manufacturing
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) is a widely recognized term across manufacturing industries, primarily known for its role in managing design data and content. But with the evolving global manufacturing landscape, PLM alone may not be enough. As production processes become increasingly complex and global, integrating PLM with Manufacturing Process Management (MPM) becomes essential for manufacturers aiming to excel.
What is MPM?
MPM is a set of methods and technologies used to streamline factory and supply chain activities. Unlike PLM, which focuses on the product design phase, MPM is concerned with how products are manufactured. It involves managing the entire manufacturing process, from planning to execution.
Key Aspects of MPM
- Product Structure Integration: MPM integrates the electronic Bill of Materials (eBOM) with the Bill of Process (BOP) or Manufacturing BOM (mBOM). While eBOM details what the product is, BOP describes how it should be manufactured.
- MPM Systems: These include Manufacturing Planning Systems, Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM), and Computer Numerical Control (CNC). These tools help define and optimize the production process.
- Process-Focused Data: MPM systems link product data with manufacturing and resource information. This connection ensures that production processes are well-defined and efficient, enhancing overall manufacturing effectiveness.
MPM Workflow
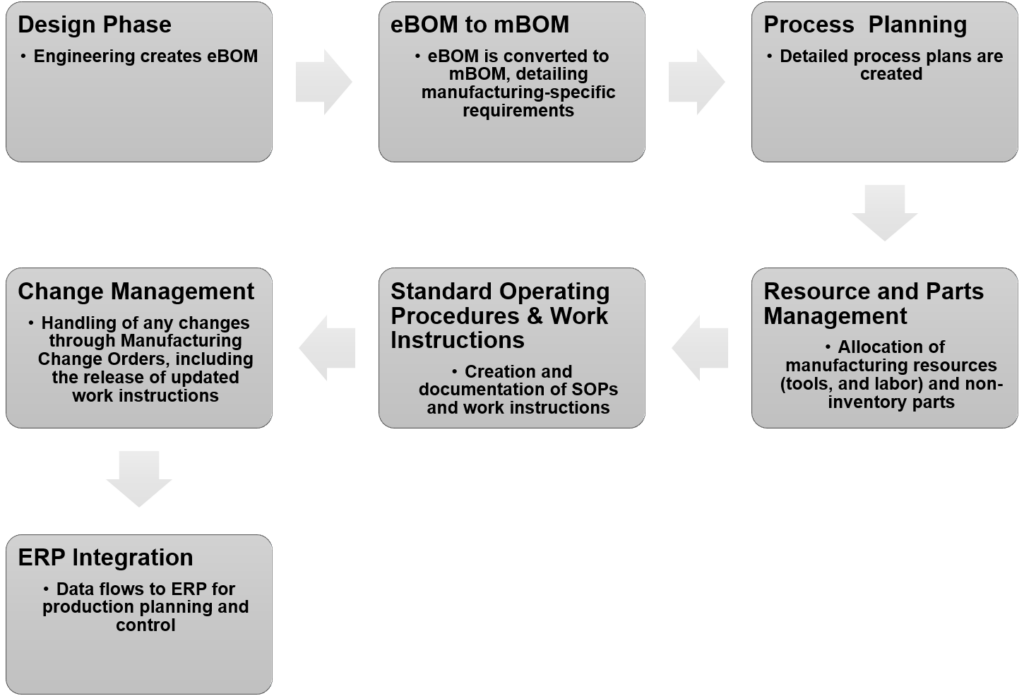
- eBOM to mBOM: Converts Engineering Bill of Materials (eBOM) to Manufacturing Bill of Materials (mBOM) and Ensures accurate translation of design specifications into manufacturing requirements.
- Process Plans: Develops comprehensive process plans detailing each step of the manufacturing process, Ensures process consistency and product quality.
- Manufacturing Resource: Manages and optimizes allocation of machinery, tools, and labor, Enhances resource utilization and reduces downtime
- Non-Inventory Parts: Tracks and plans for parts not kept in inventory but necessary for specific manufacturing tasks, Ensures timely availability of essential components.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Documents standardized operating procedures for all manufacturing processes, Enhances quality control and operational efficiency.
- Work Instructions: Provides clear, detailed instructions for each manufacturing task, Ensures accuracy and efficiency on the production floor.
- Manufacturing Change Order: Manages changes to manufacturing processes, materials, or products, Ensures systematic review, approval, and release of updated work instructions
- Production Planning Control (ERP Integration): Seamlessly flows data to ERP systems for production planning and control, Facilitates effective scheduling, resource allocation, and inventory management.
Importance of MPM
MPM acts as a critical bridge between product design and manufacturing execution. It helps translate design specifications into actionable production processes, ensuring high-quality outcomes and efficient time-to-market. By focusing on “how” to produce a product, MPM complements PLM’s focus on “what” the product is.
In today’s manufacturing world, integrating PLM with MPM is crucial for achieving optimal production performance and maintaining a competitive edge. If you’re interested in learning more about how PLM and MPM can work together, or about the eBOM to mBOM transformation, feel free to get in touch. We’re here to help!

